Delphi - Tools menu configuren met VB scripts
- Datum:
- Auteur: Stefan Cruysberghs
- Deze pagina is enkel in het Engels beschikbaar
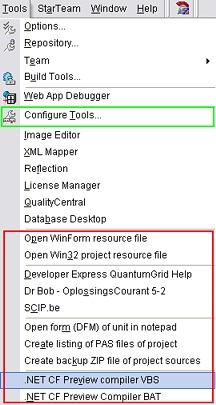 |
The Tool Properties dialog box is used to customize the Delphi Tools menu. In this article I will show a way how to create some powerful extensions for this Tools menu. Most Delphi developers like to add some extra tools like resource editors, database managers, report designers, ... I have created some Visual Basic scripts (VBScripts, VBS) to open a help file or PDF document, to open an URL in your web browser, to create a zipped backup file, to create a list of PAS files, compile your project with the .NET CF compiler, ... Hopefully this article can serve as a guideline when you start writing your own VBScripts. |
Tools Properties dialog
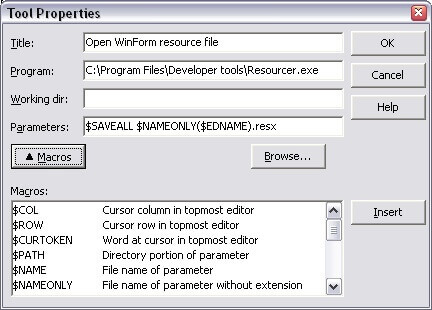
In the Tool Properties dialog you can specify the title (this is the caption of the new menu item), the location of the program, a working directory and a list of parameters.
The location of the program should include the full path to the program. The browse button can be used to search drives and directories to locate the path and file name of the program. Only EXE, COM, PIF and BAT files are allowed, other files will produce an "Unable to execute (error 2)" error upon execution.
Adding a seperator can be done by creating a new menu item and typing "-" in the title field. At first glance it seems impossible to add more then one seperator because the IDE enforces every title to be unique ("Tool called - already exists" error). This is a bug because it, clearly, doesn't count for separators. It only happens when you create a new item, not when you edit an existing one. So in order to create multiple seperators, create a new item with a non-existing title and change it afterwards.
Macros
The parameters field can be used to pass some specific parameters to the program at startup. Delphi supports 16 macros which can be used to pass some Delphi information. In Delphi 2005 the $PROJECT parameter has been added. This is interesting because now you can pass the project name to another compiler, e.g. the .NET Compact Framework compiler.
Here a list of all macros. This list is copied from the Delphi help files.
| Macro | Description |
| $COL | Expands to the column number of the cursor in the active Code editor window.For example, if the cursor is in column 50, at startup the product passes 50 to the program. |
| $ROW | Expands to the row number of the cursor in the active Code editor window.For example, if the cursor is in row 8, at startup the product passes 8 to the program. |
| $CURTOKEN | Expands to the word at the cursor in the active Code editor window. For example, if the cursor is on the word Token, at startup the product passes Token to the program. |
| $PATH | Expands to the directory portion of a parameter you specify. When you insert the $PATH macro, the product inserts $PATH() and you specify a parameter within the parentheses. For example, if you specify $PATH($EDNAME), at startup the product passes the path for the file in the active Code editor window to the program. |
| $NAME | Expands to the file name portion of a parameter you specify. When you insert the $NAME macro, the product inserts $NAME() and you specify a parameter within the parentheses. For example, if you specify $NAME($EDNAME), at startup the product passes the file name for the file in the active Code editor window to the program. |
| $NAMEONLY | Expands to the file name portion of a parameter you specify, without an extension. When you insert the $NAMEONLY macro, the product inserts $NAMEONLY() and you specify a parameter within the parentheses. |
| $EXT | Expands to the file extension portion of a parameter you specify. When you insert the $EXT macro, the product inserts $EXT() and you specify a parameter within the parentheses. For example, if you specify $EXT($EDNAME), at startup the product passes the file extension for the file in the active Code editor window to the program. |
| $EDNAME | Expands to the full file name of the active Code editor window. For example, if you are editing the file C:\PROJ1\UNIT1.PAS, at startup the product passes C:\PROJ1\UNIT1.PAS to the program. |
| $EXENAME | Expands to the full file name of the current project target. For example, if you are working on the project PROJECT1 in C:\PROJ1, at startup the product passes C:\PROJ1\PROJECT1.EXE to the program. If you are working on a package project PACKAGE1 in C:\PACKAGE, at startup the product passes C:\PACKAGE\PACKAGE1.BPL to the program. |
| $HOSTNAME | Expands to the full file name of the executable which is run for the current project. For .executable projects, this macro is equivalent to the $EXENAME macro. For package and DLL projects, this macro expands to the project's host application as defined on the Run|Parameters dialog box. For example, if you are working on the project PROJECT1 in C:\PROJ1, at startup the product passes C:\PROJ1\PROJECT1.EXE to the program. If you are working on a package project called PACKAGE1 in C:\PACKAGE, and the host application is set to C:\HOST\HOSTAPP.EXE at startup the product passes "C:\HOST\HOSTAPP.EXE" to the program (rather than the package name "C:\PACKAGE\PACKAGE1.BPL"). |
| $PARAMS | Expands to the command-line parameters specified in the Run Parameters dialog box. |
| $PROJECT | NEW IN DELPHI 2005. Expands to the file name of the current project. |
| $PROMPT | Prompts you for parameters at startup. When you insert the $PROMPT macro, the product inserts $PROMPT() and you specify a default parameter within the parentheses. |
| $SAVE | Saves the active file in the Code editor. |
| $SAVEALL | Saves the current project. |
| $TDW | Sets up your environment for running Turbo Debugger. For example, this macro saves your project, ensures that your project is compiled with debug info turned on, and recompiles your project if it is not compiled with debug info turned on. Be sure to use this macro if you add Turbo Debugger to the Tools menu. |
Some examples :
Open resource file of current .NET WinForms unit
I like the tool Resourcer (Lutz Roeder, http://www.aisto.com/roeder/dotnet) and I'm utilizing it to take a look at .NET resource files. By using a combination of some macros the resource file of the current WinForms unit can be opened.
| Program | C:\Program Files\Developer tools\Resourcer.exe |
| Parameters | $SAVEALL $NAMEONLY($EDNAME).resx |
Open resource file of current Win32 project
For openening the Win32 resource file of a Delphi project I'm using an older tool called ResourceHacker (Angus Johnson, http://www.angusj.com/resourcehacker).
| Program | C:\Program Files\Developer tools\ResHacker.exe |
| Parameters | $SAVEALL $NAMEONLY($PROJECT).res |
VB scripts
The program field only allows EXE, COM, PIF and BAT (which is not visible in filter combobox) files. That is a pitty, because you can't create a link to another type of file. But by passing an unit name ($EDNAM) or project name ($PROJECT) to a VB script you can create some powerful extensions for Delphi. Some examples :
Open given file (help, pdf, ...) or URL
I've created a very small VB script to open a help file, PDF document, Word document, image or URL. The filename or URL will be passed to the script and by using the Windows Shell Run method the associated program will be started.
| Program | C:\WINDOWS\system32\wscript.exe |
| Parameters | "C:\Program Files\Borland\BDS\3.0\Scripts\OpenFileURL.vbs" "C:\Program Files\Developer Express.VCL\ExpressQuantumGrid 5\Help\EXPRESSQUANTUMGRID.HLP" |
| Program | C:\WINDOWS\system32\wscript.exe |
| Parameters | "C:\Program Files\Borland\BDS\3.0\Scripts\OpenFileURL.vbs" "D:\Books\Dr Bob - Delphi OplossingsCourant 5-2.pdf" |
| Program | C:\WINDOWS\system32\wscript.exe |
| Parameters | "C:\Program Files\Borland\BDS\3.0\Scripts\OpenFileURL.vbs" "http://www.scip.be" |
OpenFileURL.vbs
Dim WshShell, Args
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Set Args = WScript.Arguments
If Args.Count = 0 Then
MsgBox "No file given", 16, "Error"
Else
WshShell.Run(Chr(34) & Args(0) & Chr(34))
End If
Open DFM from given unit
Sometimes a DFM file gets corrupted. Then you have to open it with an external editor. This small script will open the DMF file of the current PAS file.
| Program | C:\WINDOWS\system32\wscript.exe |
| Parameters | "C:\Program Files\Borland\BDS\3.0\Scripts\OpenFormOfUnit.vbs" $EDNAME |
OpenFormOfUnit.vbs
Dim WshShell, Fso, Args
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Set Fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Args = WScript.Arguments
If Args.Count = 0 Then
MsgBox "No unit given", 16, "Error"
Else
q = Chr(34) 'quote
strUnitName = Fso.GetBaseName(Args(0))
strUnitFolder = Fso.GetParentFolderName(Args(0))
' Set DFM filename from given PAS filename
strForm = strUnitFolder & "\" & strUnitName & ".dfm"
If Not Fso.FileExists(strForm) Then
MsgBox "Unit has no form (" & strUnitName & ")", 16, "Error"
Else
WshShell.Run("notepad " & q & strForm & q)
End If
End If
Create list of all PAS files in given project folder
This script will create a listing of all PAS files in the project folder. This list will be created by executing the DOS DIR command. The result will be redirected to a log file and at the end this file will be opened with the associated editor (notepad, ultraedit, ...)
| Program | C:\WINDOWS\system32\wscript.exe |
| Parameters | "C:\Program Files\Borland\BDS\3.0\Scripts\ListPASFiles.vbs" $PROJECT |
ListPASFiles.vbs
Dim WshShell, Fso, Args
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Set Fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Args = WScript.Arguments
If Args.Count = 0 Then
MsgBox "No project given", 16, "Error"
Else
q = Chr(34) 'quote
strProjectFolder = Fso.GetParentFolderName(Args(0))
strLogFileName = strProjectFolder & "\ListPasFilesLog.txt"
strCommandLine = "cmd /c > " & q & strLogFileName & q & " dir /b " & q & strProjectFolder & "\*.pas"
' Execute dir command and save result in log file
WshShell.Exec(strCommandLine)
' Open log file
WshShell.Run(strLogFileName)
End If
Create backup ZIP file of given project folder
Sometimes it can be useful to create a temporary backup of your source code, even if you are using a version control system. So I needed a small script which will backup my sources in a ZIP file and store it with a unique name (with date and time) in my backup folder.
For creating ZIP files within a VB script, I'm using the Winzip command line add-on. This is a small executable with the name WZZIP.EXE. It can be started with a lot of command line parameters. Because the command window is closed after executing, you can't see the result. So I always redirect the command (DOS) output to a log file.
| Program | C:\WINDOWS\system32\wscript.exe |
| Parameters | $SAVEALL "C:\Program Files\Borland\BDS\3.0\Scripts\BackupProject.vbs" $PROJECT |
BackupProject.vbs
Dim WshShell, Fso, Args
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Set Fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Args = WScript.Arguments
Function GetDateTimePart(strPart)
GetDateTimePart = DatePart(strPart,Now())
If Len(GetDateTimePart) < 2 Then
GetDateTimePart = "0" & GetDateTimePart
End If
End Function
' Create datetime string yyyymmdd_hhnn
Function GetFormattedDateTime
GetFormattedDateTime = GetDateTimePart("yyyy") & GetDateTimePart("m") & GetDateTimePart("d")
& "_" & GetDateTimePart("h") & GetDateTimePart("n")
End Function
If Args.Count = 0 Then
MsgBox "No project given", 16, "Error"
Else
q = Chr(34)
' Set paths and filenames
strProjectName = Fso.GetBaseName(Args(0))
strProjectFolder = Fso.GetParentFolderName(Args(0))
strZipExe = "C:\Program Files\Winzip\WZZIP.exe"
strBackupFolder = "D:\Backup"
strZipLogFileName = strBackupFolder & "\BackupProjectLog.txt"
' Set name of zip file with project name and date and time
strZipFileName = strBackupFolder & "\" & strProjectName & "_" & GetFormattedDateTime & ".zip"
' Create backup folder if it does not exists
If Not Fso.FolderExists(strBackupFolder) Then
Fso.CreateFolder(strBackupFolder)
End If
' Create ZIP file in backup folder and save log file
strCommandLine = "cmd /c > " & q & strZipLogFileName & q & " " & q & strZipExe & q
& " -r -p " & q & strZipFileName & q & " " & q & strProjectFolder & q
WshShell.Exec(strCommandLine)
End If
Compile application with DCCIL.exe (.NET CF preview compiler)
In David Cleggs Delphi for .NET Compact Framework Preview Quickstart Guide he shows a batch file to compile a Delphi .NET application with the Borland .NET Compact Framework Preview Compiler (DCCIL.EXE). The result of the compilation will be shown in a command window.
Nice, but it would be better if the result is saved in a log file. So I have written a VB script which does the same but the output is redirected to a log file and afterwards this log file will be opened. I have chosen to use the "PAS" extension for the log file so it will open in my Delphi IDE. This makes it easier to solve the errors which are outputted by the .NET CF compiler.
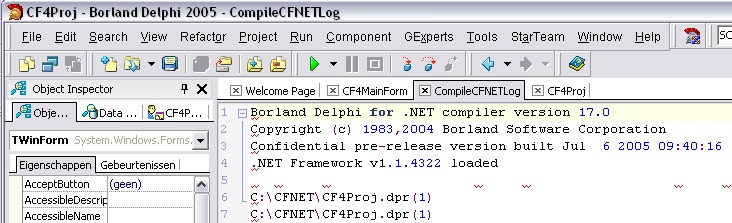
| Program | C:\WINDOWS\system32\wscript.exe |
| Parameters | $SAVEALL "path\CompileNETCF.vbs" $NAMEONLY($PROJECT) $PATH($PROJECT) |
CompileNETCF.vbs
' CompileNETCF.VBS
' Compile project with Delphi 2005/2006 .NET Compact Framework Compiler (DCCIL)
' August 2005 / February 2006 - Stefan Cruysberghs
' Delphi tools properties
' * Program : C:\WINDOWS\system32\wscript.exe
' * Parameters : $SAVEALL "path\CompileNETCF.vbs" $NAMEONLY($PROJECT) $PATH($PROJECT)
Dim WshShell, Fso, Args, Exec, i
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Set Fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
Set Args = WScript.Arguments
If Args.Count = 0 Then
MsgBox "No Delphi project given", 16, "Error"
Else
strProjectName = Args(0)
strProjectFolder = ""
For i = 1 To Args.Count-1
strProjectFolder = strProjectFolder & " " & Args(i)
Next
strProjectName = Trim(Fso.GetBaseName(strProjectName))
strProjectFolder = Trim(Fso.GetParentFolderName(strProjectFolder))
strProject = strProjectFolder & "\" & strProjectName & ".dpr"
If Not Fso.FileExists(q & strProject & q) Then
MsgBox strProject & " does not exist", 16, "Error"
Else
q = Chr(34) 'quote
' Set paths Delphi 2006
strDCCIL = "C:\Program Files\Borland\BDS\4.0\Bin\dccil.exe"
strCFUnits = "C:\Program Files\Borland\BDS\4.0\lib\cf"
' Set paths Delphi 2005
' strDCCIL = "C:\Program Files\Borland\BDS\3.0\CFPreview\Bin\dccil.exe"
' strCFUnits = "C:\Program Files\Borland\BDS\3.0\CFPreview\Lib"
strLogFileName = strProjectFolder & "\CompileCFNETLog.pas"
' Extra compiler options. If .NET CF assemblies are not available/needed, set it to ""
strCompilerOptions = ""
'strCompilerOptions = " -lu" & q & "C:\NETCFAssemblies\Microsoft.WindowsCE.Forms.dll"
' & q & " -lu" & q & "C:\NETCFAssemblies\System.Windows.Forms.DataGrid.dll" & q
' Delete all .dcuil files
On Error Resume Next
Fso.DeleteFile strProjectFolder & "\*.dc?il", True
strCommandLine = "cmd /c > " & q & strLogFileName & q & " " & q & strDCCIL & q & " "
& q & strProject & q & " -u" & q & strCFUnits & q
& " -luSystem.Windows.Forms -luSystem.Data " & strCompilerOptions
' Compile the project with the DCCIL.exe
Set Exec = WshShell.Exec(strCommandLine)
' Wait for application to exit
Do While Exec.Status = 0
WScript.Sleep 1
Loop
' Show the log file (when extention of log is PAS, it will be opened in Delphi)
WshShell.Run(q & strLogFileName & q)
End If
End IfRemove the enters in the command line rule because this should be one source line !
Registry
If you like to take a backup of your customized tools menu, then you have to export the Transfer keys in the Windows registry.
Delphi 7
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Borland\Delphi\7.0\Transfer
Delphi 2005
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Borland\BDS\3.0\Transfer
Delphi 2006
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Borland\BDS\4.0\Transfer
Afterwards you can import the REG file on other Delphi developer PC's or on your own PC after a clean install.
